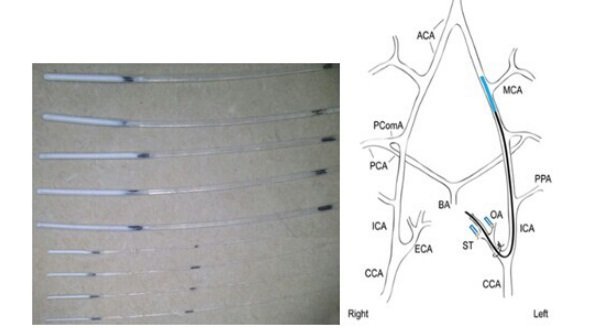
小鼠MCAO模型 栓线
产品名称: 小鼠MCAO模型 栓线
英文名称: 小鼠MCAO模型 栓线
产品编号: Doccol线拴/小鼠 MCAO线栓/脑缺
产品价格: 0
产品产地: USA
品牌商标: 玉研科学仪器有限公司
更新时间: 2023-08-17T15:24:17
使用范围: null
上海玉研科学仪器有限公司
- 联系人 : 方经理
- 地址 : 上海市闵行区兴梅路485号中环科技园301室
- 邮编 : 200237
- 所在区域 : 上海
- 电话 : 185****9044 点击查看
- 传真 : 点击查看
- 邮箱 : sales@yuyanbio.com
动物大脑中动脉栓塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion, MCAO)模型是目前使用最为广泛的、研究局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤的理想模型。线栓法是制作MCAO模型常用方法,MCAO线栓(MCAO Monofilaments, MCAO Sutures)则是制备大鼠、小鼠(或其它实验动物)这一模型非常关键的实验材料,本产品采用柔韧度非常好的进口单丝尼龙线,经显微操作,头端均匀包被硅胶,其表面光滑,粗细一致,易进入颅内又不至于刺破血管,使用本产品可大大提高模型制备的成功率,及脑缺血范围的稳定性。
对于MCAO模型来说,主要有两种线拴,无包被的火焰熔烫圆头线拴及硅胶包被线拴。研究表明(Tsuchiya et al. 2003),无包被的圆头线拴在MCAO实验过程中可能导致高达40%的蛛网膜下腔出血,而其标准差可能比平均值的50%还要大。另一项技术文章表明(Shimamura et al. 2006a),硅胶包被线拴要远好于无包被的圆头线拴,其结果更为稳定,即使对于没有经验的实验者来说也是如此。而多聚赖氨酸包被的线拴只能增加死亡率,不能减少梗赛体积的变异程度(Huang et al. 1998)。
Doccol MCAO线拴全部为硅胶包被,圆润、柔软、包被均匀,即使在没有激光多普勒实时检测的情况,也不会将血管戳破。使用自制的硅胶包被的线拴,大鼠(Schmid-Elsaesser et al. 1998)及小鼠(Shah et al. 2006)的脑梗塞体积的标准差均在30%左右。而使用Doccol MCAO线拴可以得到更好的结果。对于大鼠MCAO模型来说,使用Doccol MCAO线拴得到的结果的标准差可达10%-20% (Ruscher et al.2012;Ishizaka et al.2013;Sakata et al.2012;Candelario-Jalil et al. 2008;Khan et al. 2006;Liu et al. 2006;Shimamura et al. 2006b;Solaroglu et al. 2006;Tsubokawa et al. 2007;Tsubokawa et al. 2006a;Tsubokawa et al. 2006b)。对于小鼠来说,使用Doccol MCAO线拴得到的结果的标准差可达5%-10%(Chen et al.2014; Bae et al.2013; Jin et al.2011; Gu et al.2012; Kleinschnitz et al. 2007; Maysami et al. 2008; Pignataro et al. 2007b; Pignataro et al. 2007c)。
References1. Bae ON, Serfozo K, Baek SH, et al. (2013) Safety and efficacy evaluation of carnosine, an endogenous neuroprotective agent for ischemic stroke. Stroke 44(1):205-12.2. Candelario-Jalil E, Munoz E, Fiebich BL. (2008) Detrimental effects of tropisetron on permanent ischemic stroke in the rat. BMC Neurosci 9:193. Chen HZ, Guo S, Li ZZ, et al. (2014) A critical role for interferon regulatory factor 9 in cerebral ischemic stroke.J Neurosci.34(36):11897-912.4. Huang J, Kim LJ, Poisik A, Pinsky DJ, Connolly ES, Jr. (1998) Does poly-L-lysine coating of the middle cerebral artery occlusion suture improve infarct consistency in a murine model? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 7:296-3015. Gu L, Xiong X, Zhang H, et al. (2012) Distinctive Effects of T Cell Subsets in Neuronal Injury Induced by Cocultured Splenocytes In Vitro and by In Vivo Stroke in Mice. Stroke 43:1941-1946.6. Ishizaka S, Horie N, Satoh K, et al. (2013) Intra-arterial Cell Transplantation Provides Timing-Dependent Cell Distribution and Functional Recovery After Stroke. Stroke 44:720-726.7. Jin R, Song Z, Yu S, et al. (2011) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke.Stroke 42(7):2033-44.8. Khan M, Jatana M, Elango C, Paintlia AS, Singh AK, Singh I. (2006) Cerebrovascular protection by various nitric oxide donors in rats after experimental stroke. Nitric Oxide 15:114-1249. Kleinschnitz C, Pozgajova M, Pham M, Bendszus M, Nieswandt B, Stoll G. (2007) Targeting platelets in acute experimental stroke: impact of glycoprotein Ib, VI, and IIb/IIIa blockade on infarct size, functional outcome, and intracranial bleeding. Circulation 115:2323-233010. Koizumi J, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T, Ooneda G. (1986) Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema, I: a new experimental model of cerebral embolism in rats in which recirculation can be introduced in the ischemic area. Jpn J Stroke 8:1-811. Liu S, Liu W, Ding W, Miyake M, Rosenberg GA, Liu KJ. (2006) Electron paramagnetic resonance-guided normobaric hyperoxia treatment protects the brain by maintaining penumbral oxygenation in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1274-128412. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84-9113. Maysami S, Lan JQ, Minami M, Simon RP. (2008) Proliferating progenitor cells: a required cellular element for induction of ischemic tolerance in the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1104-111314. Pignataro G, Simon RP, Boison D. (2007a) Transgenic overexpression of adenosine kinase aggravates cell death in ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1-515. Pignataro G, Simon RP, Xiong ZG. (2007b) Prolonged activation of ASIC1a and the time window for neuroprotection in cerebral ischaemia. Brain 130:151-15816. Pignataro G, Studer FE, Wilz A, Simon RP, Boison D. (2007c) Neuroprotection in ischemic mouse brain induced by stem cell-derived brain implants. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:919-92717. Ruscher K, Kuric E, Wieloch T, et al. (2012) Levodopa Treatment Improves Functional Recovery After Experimental Stroke. Stroke 43:507-513.18. Sakata H, et al. (2012) Minocycline-Preconditioned Neural Stem Cells Enhance Neuroprotection after Ischemic Stroke in Rats. J Neurosci. 32(10):3462–3473.19 Schmid-Elsaesser R, Zausinger S, Hungerhuber E, Baethmann A, Reulen HJ. (1998) A critical reevaluation of the intraluminal thread model of focal cerebral ischemia: evidence of inadvertent premature reperfusion and subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats by laser-Doppler flowmetry. Stroke 29:2162-217020. Shah ZA, Namiranian K, Klaus J, Kibler K, Dore S. (2006) Use of an optimized transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery protocol for the mouse stroke model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 15:133-13821. Shimamura N, Matchett G, Tsubokawa T, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. (2006a) Comparison of silicon-coated nylon suture to plain nylon suture in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J Neurosci Methods 156:161-16522. Shimamura N, Matchett G, Yatsushige H, Calvert JW, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. (2006b) Inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 ameliorates focal cerebral ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Stroke 37:1902-190923. Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Cahill J, Zhang JH. (2006) Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 143:965-97424. Tsubokawa T, Jadhav V, Solaroglu I, Shiokawa Y, Konishi Y, Zhang JH. (2007) Lecithinized superoxide dismutase improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats. Stroke 38:1057-106225. Tsubokawa T, Solaroglu I, Yatsushige H, Cahill J, Yata K, Zhang JH. (2006a) Cathepsin and calpain inhibitor E64d attenuates matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 37:1888-189426. Tsubokawa T, Yamaguchi-Okada M, Calvert JW, Solaroglu I, Shimamura N, Yata K, Zhang JH. (2006b) Neurovascular and neuronal protection by E64d after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci Res 84:832-84027. Tsuchiya D, Hong S, Kayama T, Panter SS, Weinstein PR. (2003) Effect of suture size and carotid clip application upon blood flow and infarct volume after permanent and temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 970:131-139
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
TEL : 021-35183767 , 18502129044
QQ : 2113136797
Mail: yuyan0317@126.com
敬请来电咨询!




